1. Running Inline Monitor Applications for Microbenchmarking Experiments¶
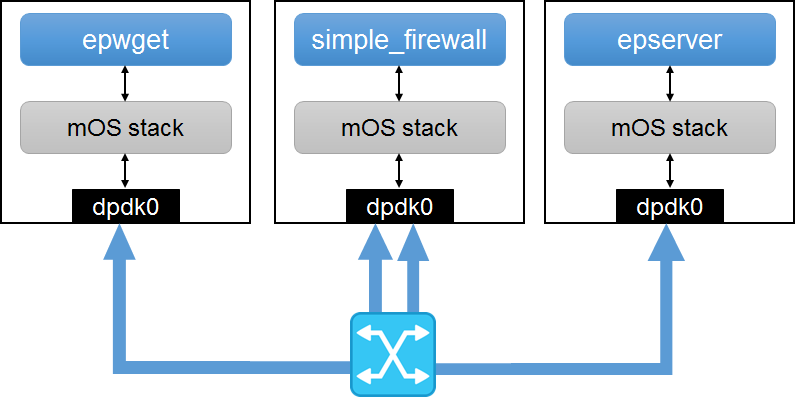
This page describes how one can set up a mOS inline middlebox for microbenchmarking experiments. In this setup, we assume that the client(s) and the server(s) are only two network hops away from each other and the mOS middlebox application serves as a proxy of each peer node (whether it is a client or a server). The following figure explains the setup with more clarity.
1.1. Environment¶
where:
- The client is connected to switch port #1,
- The middlebox is connected to switch port #2,
- The server is connected to switch port #3.
All 3 hosts are considered to be set up in local area network (LAN) settings with an Ethernet switch. Each endpoint (client and server) exchanges traffic by sending Ethernet frames with destination MAC address of the middlebox’s NIC. The mOS networking core transparently updates the destination MAC addresses of either node as the packet is forwarded in both directions. The startup mOS configuration file needs to be adjusted for Ethernet maquerading accordingly.
Please follow the directions in Compiling the mOS net library to set up the mOS net library & the environment and refer to Compile and run sample applications to ensure that you successfully compile the mOS application.
- In the middlebox, please compile simple_firewall.
1.1.1. Static MAC address table setup¶
We need to carefully set up static ARP table entries to make all traffic between the client (node A) and the server (node B) propogate via the middlebox (node M). You can use ‘arp’ command to set a static ARP table entry of A, B and M. mOS networking core will read Linux kernel’s ARP entry during its initialization phase.
For A:
$ arp -s <B_IP_ADDR> <M_MAC_ADDR>
For B:
$ arp -s <A_IP_ADDR> <M_MAC_ADDR>
For the middlebox:
$ arp -s <A_IP_ADDR> <A_MAC_ADDR>
$ arp -s <B_IP_ADDR> <B_MAC_ADDR>
1.1.2. Switch’s forwarding table setup¶
Port# MAC address 1 A_MAC_ADDR2 M_MAC_ADDR3 B_MAC_ADDR
1.1.3. Setup mOS application configurations¶
Before running the simple_firewall application, you need to update the configuration files in the middlebox.
- In M, specify the L3/L4 firewall rules in
simple_firewall.conf(please refer to the example configration file below).
# Simple firewall rules
#(act) (src) (dst) (port)
DROP 10.0.0.0/24 10.1.0.0/24 dport:80
ACCEPT 10.0.1.7 10.1.1.9 sport:1024
ACCEPT 10.0.2.7 10.1.2.9
ACCEPT 10.0.3.0/24 10.1.3.0/24
- In the middlebox, please configure
mos.confas below. We assume that the node uses CPU core 0~7 for running mOSsimple_firewall. Please make sure that you setforward = 1to allow thesimple_firewallapplication to forward the traffic if the ruleset permits. Also set thearp_tableand theroute_tableentries appropriately. Please note that the ARP learning submodule of mOS networking core is disabled for this setup.
#######################
# MOS-RELATED OPTIONS #
#######################
mos {
forward = 1
#######################
##### I/O OPTIONS #####
#######################
# number of memory channels per socket [mandatory for DPDK]
nb_mem_channels = 4
# devices used for MOS applications [mandatory]
netdev {
dpdk0 0x00FF
dpdk1 0x00FF
}
#######################
### LOGGING OPTIONS ###
#######################
# NICs to print network statistics per second
# if enabled, mTCP will print xx Gbps and xx pps for RX and TX
stat_print = dpdk0 dpdk1
# A directory contains MOS system log files
mos_log = logs/
}
1.2. Run simple_firewall¶
In M, run simple_firewall with sudo privileges. You would see
the application block TCP flows according to the rules specified in
simple_firewall.conf.
$ sudo ./simple_firewall
1.3. Troubleshooting¶
If your mOS program crashes, search through the printed log messages to check if you missed any of the following requirements:
- You should load only the dpdk-registered interfaces (after loading the
igb_uiodriver) and configure hugepages as described in Compiling the mOS net library.- You should create a log folder specified in
mos_logparameter inmos.conf(logs/in our example) within the same directory that contains the mOS application binary.- Please check if your system is running out of memory by looking at the memory footprint (OOM errors). If you have memory deficiency issues, please reduce the number of socket buffers in
mos.conf.
If the traffic fails to pass through Host 1, check the following issues:
- Check whether you achieve connectivity by reverting back to kernel network driver for the interfaces (see option 5 in Configure runtime environment for mOS applications with DPDK). You can try testing your setup as a network bridge with default Linux kernel network drivers.
1.3.1. Compile and build mOS library and application (on M)¶
Please refer to Compiling the mOS net library and Building mOS Applications.
1.3.2. Run ‘simple_firewall’ (on M)¶
$ sudo ./simple_firewall
1.3.3. Run web server (on A)¶
You can setup Nginx or Apache web server for this test. See http://nginx.org or http://www.apache.org for further information.
1.3.4. Run Wget (on B)¶
$ wget http://ipaddress:port/